Understanding OSA and Emerging Treatment Options

What is OSA?
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a condition characterized by repeated episodes of pharyngeal collapse during sleep, leading to apnea (pauses in breathing) and hypopneas (shallow breathing). These episodes cause reduced oxygen levels in the blood (hypoxemia) and increased carbon dioxide levels (hypercapnia), triggering recurrent arousals during sleep.
In simpler terms, when oxygen levels drop, the Reticular Activating System in the brainstem sends signals that briefly awaken you just enough to resume breathing. This constant shift from deep sleep to lighter stages significantly disrupts sleep quality.
Deep sleep, also known as Stage 3 NREM sleep, is vital for brain health, memory consolidation, and cognitive performance. Consequently, chronic reduction in deep sleep leads to daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and concentration difficulties.

Current Treatment Options for OSA
Doctors often recommend the following treatment approaches:
- Lifestyle Changes: Weight loss through improved diet, exercise, and behavioral modifications.
- CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure): A mechanical ventilation system that maintains open airways by providing a constant airflow.
While CPAP has demonstrated effectiveness in reducing the apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) and improving OSA symptoms, it has not significantly improved cardiovascular outcomes or reduced mortality rates.
Why Is This Study on Tirzepatide Important?
Tirzepatide is known for its ability to treat obesity and diabetes while also promoting weight loss. Researchers explored whether this dual-action medication could also improve OSA outcomes and related cardiovascular risks.
This investigation was particularly crucial for two reasons:
- CPAP’s Limited Impact on Cardiovascular Outcomes: While CPAP addresses the immediate symptoms of OSA, its effects on long-term cardiovascular health have been limited.
- Mild OSA Cases (AHI 5-15): For patients with mild OSA, CPAP therapy is not typically recommended. This highlights the need for alternative treatments.
Study Findings: How Tirzepatide Showed Promise
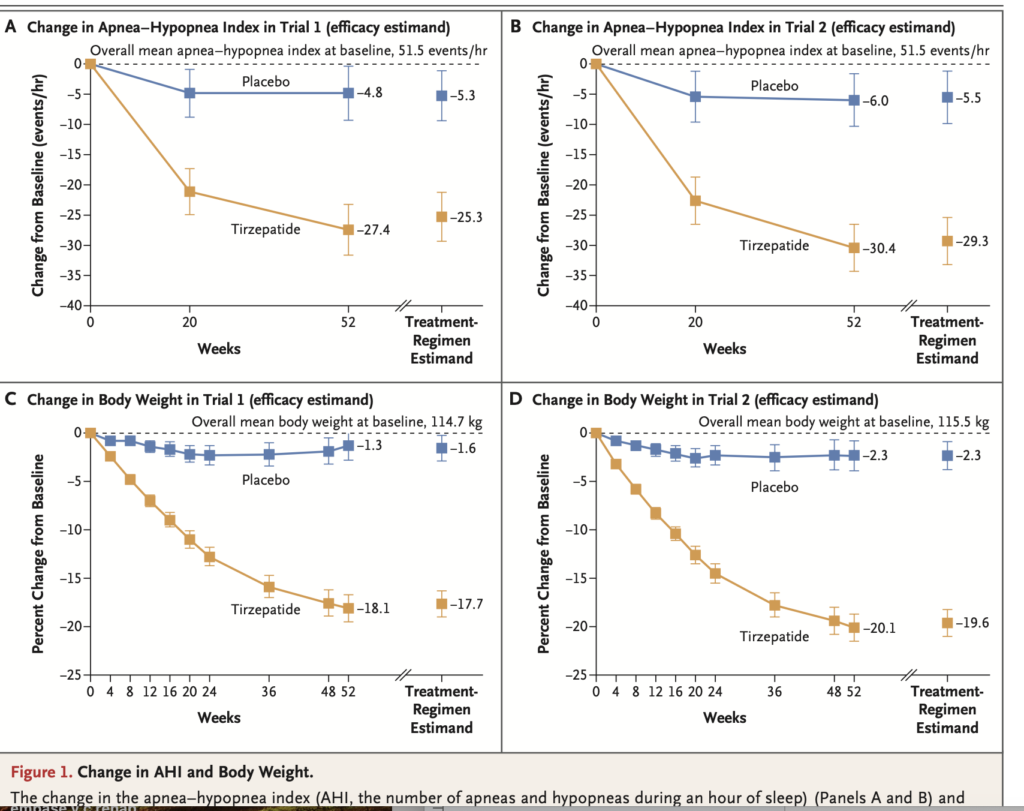
The randomized controlled trial (RCT) conducted over 52 weeks demonstrated impressive results. Among participants who received tirzepatide, up to 50.2% in both SURMOUNT-OSA trials met the criteria of experiencing fewer than 5 AHI events per hour or between 5 to 14 AHI events per hour. This finding emphasizes tirzepatide’s potential role as a first-line alternative to CPAP.
Key Results from the Study
- Significant reduction in sleep-disordered breathing episodes.
- Improved perceived sleep quality and reduced disruption.
- Notable improvements in OSA-related cardiovascular risk factors.
Conclusion:
This study underscores the potential of tirzepatide as a viable alternative treatment for individuals with mild to moderate OSA, particularly those who may not be candidates for CPAP therapy. As OSA continues to pose a major risk to both sleep quality and cardiovascular health, these findings mark a promising step toward more effective and comprehensive treatment options.
